Understanding True Health & Healing
Discover the fundamental differences between alternative and conventional medicine, and learn how addressing root causes through nutrition and natural healing can transform your health.
Understanding The Difference
Alternative Medicine vs. Conventional Medicine
While conventional medicine focuses on treating symptoms, alternative medicine seeks to identify and resolve the underlying root causes of health issues.
The Fundamental Difference
Conventional medicine often provides quick relief by covering symptoms—like using painkillers for headaches or medications for high blood pressure. However, this approach doesn't address why the problem exists in the first place. Alternative medicine takes a different path: it investigates the root cause, whether it's nutritional deficiencies, lifestyle factors, or imbalances in the body, and works to correct these underlying issues naturally.
| Aspect | Alternative Medicine | Conventional Medicine |
|---|---|---|
| Approach | Addresses root causes of illness | Treats symptoms and manages conditions |
| Focus | Whole-body wellness and prevention | Disease-specific treatment |
| Methods | Natural remedies, nutrition, lifestyle changes | Pharmaceutical drugs and surgery |
| Goal | Restore body's natural healing ability | Suppress or eliminate symptoms |
| Side Effects | Minimal, natural healing process | Often significant medication side effects |
Foundation of Health
Vitamins, Food & The Basics of Being Healthy
True health begins with understanding and providing your body with the essential nutrients and conditions it needs to thrive naturally.

Food as Medicine: Your Body's Natural Pharmacy
Every vitamin, mineral, and nutrient you consume plays a specific role in your body's complex systems. When you provide your body with the right nutrients through whole foods and proper supplementation, you give it the tools it needs to heal itself naturally.
Unlike synthetic medications that often come with side effects, vitamins and nutrients from food work in harmony with your body's natural processes. They don't just mask symptoms—they support your body's innate ability to maintain balance and health.
Vitamins & Minerals
Essential micronutrients that support every bodily function, from immune health to energy production.
Whole Foods
Natural, unprocessed foods provide the building blocks your body needs for optimal health and healing.
Proper Hydration
Water is essential for nutrient transport, detoxification, and maintaining every cellular process.
Lifestyle Balance
Sleep, stress management, and physical activity are fundamental to maintaining health.
The Mind-Gut Connection
The Powerful Relationship Between Your Stomach & Brain
Your gut and brain are in constant communication through a complex network that influences your mood, mental health, and overall well-being.
Your "Second Brain"
Scientists call the gut the "second brain" because it contains over 100 million neurons—more than in your spinal cord. This enteric nervous system doesn't just control digestion; it communicates directly with your brain through the gut-brain axis.
This bidirectional communication means that your gut health directly affects your mental state, and your mental state affects your gut health. Stress, anxiety, and depression can manifest as digestive issues, while poor gut health can contribute to mood disorders.
Key Insight
When you heal your gut, you're not just improving digestion—you're supporting your mental health, immune system, and overall vitality.
The Gut-Brain Axis
Neural Pathway
The vagus nerve serves as the main communication highway between gut and brain
Chemical Messengers
Gut bacteria produce neurotransmitters that affect mood and cognition
Immune Connection
70% of your immune system resides in your gut, influencing inflammation and health
Signs of Poor Gut-Brain Connection
- •Anxiety and depression
- •Brain fog and poor concentration
- •Mood swings and irritability
- •Digestive issues and bloating
How to Support Gut-Brain Health
- •Eat probiotic-rich fermented foods
- •Consume prebiotic fiber for gut bacteria
- •Manage stress through meditation and exercise
- •Avoid processed foods and excess sugar
The Master Nerve
The Vagus Nerve: Your Body's Superhighway
The vagus nerve is the longest cranial nerve in your body, serving as the primary communication channel between your brain and gut.
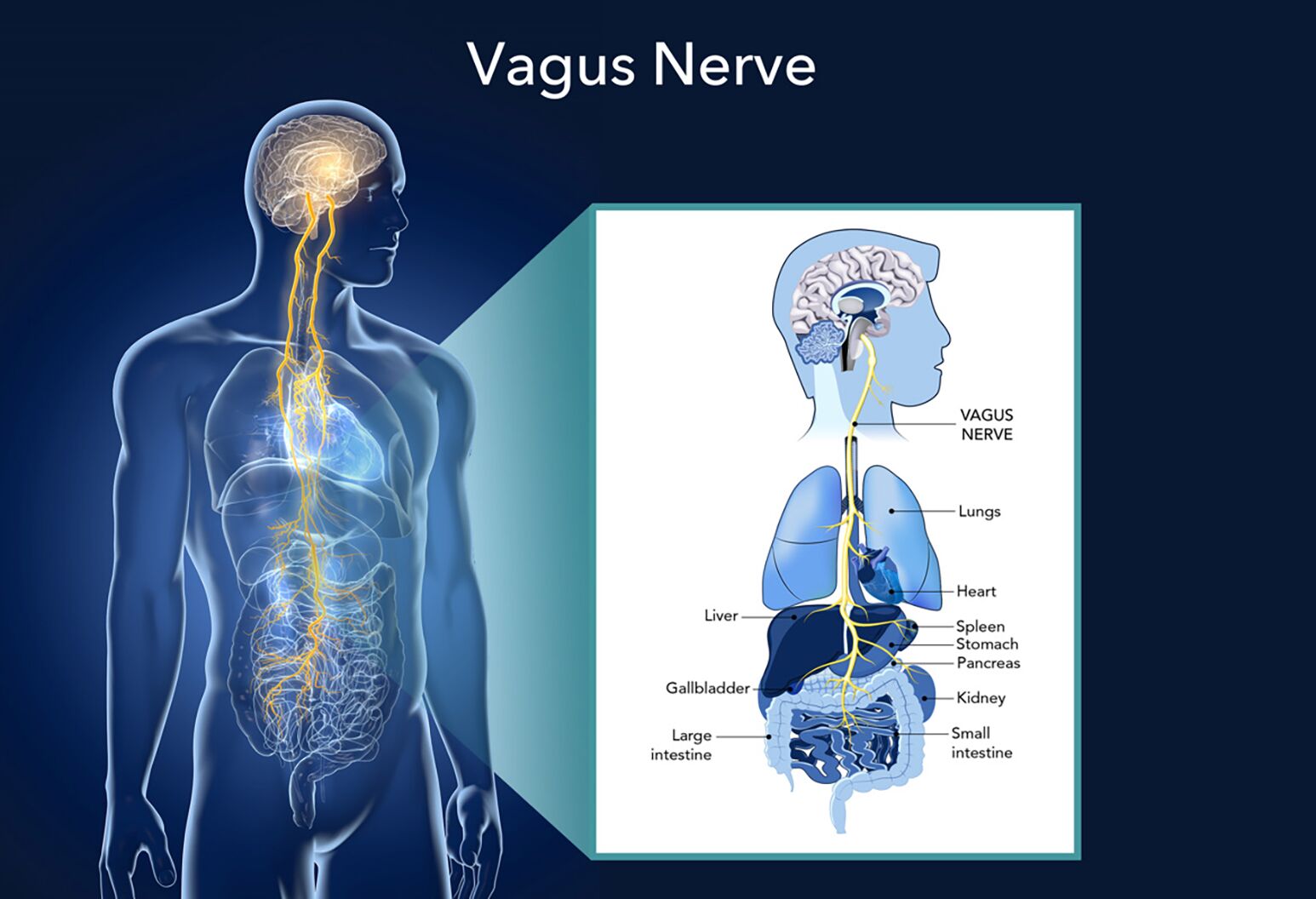
What is the Vagus Nerve?
The vagus nerve is like a superhighway of information running from your brainstem down through your neck, chest, and abdomen. It's responsible for controlling many automatic functions in your body, including:
- •Heart rate and blood pressure
- •Breathing and respiratory function
- •Digestive processes and gut function
- •Immune system response
- •Mood and emotional regulation
The Gut-Brain Communication Highway
About 80-90% of the vagus nerve fibers carry information FROM your gut TO your brain, not the other way around. This means your gut is constantly sending signals to your brain about your digestive health, nutrient status, and even the state of your gut bacteria.
When your vagus nerve is functioning optimally (high vagal tone), you experience better digestion, reduced inflammation, improved mood, and enhanced stress resilience. Poor vagal tone is associated with digestive disorders, anxiety, depression, and chronic inflammation.
Ways to Stimulate Your Vagus Nerve:
- ✓Deep breathing exercises and meditation
- ✓Cold exposure (cold showers or ice baths)
- ✓Singing, humming, or gargling
- ✓Probiotics and gut-healthy foods
- ✓Regular exercise and yoga
Heart Rate Regulation
Controls heart rate variability and cardiovascular health
Digestive Control
Manages digestive processes and gut motility
Inflammation Response
Regulates immune response and reduces inflammation
The Happiness Connection
Gut Bacteria & Serotonin: The 90% Secret
Your gut bacteria produce over 90% of your body's serotonin—the neurotransmitter responsible for mood, happiness, and well-being.
Your Gut: The Happiness Factory
While most people think of serotonin as a brain chemical, the surprising truth is that approximately 90-95% of your body's serotonin is actually produced in your gut by the trillions of bacteria living there.
These beneficial gut bacteria don't just produce serotonin—they also create other important neurotransmitters like dopamine, GABA, and norepinephrine. This is why gut health has such a profound impact on mental health, mood disorders, anxiety, and depression.
The 90% Rule
When you improve your gut health through proper nutrition and probiotics, you're directly supporting your body's natural production of mood-regulating neurotransmitters.
How Gut Bacteria Affect Your Mood & Mental Health
Mood Regulation
Healthy gut bacteria produce serotonin and other neurotransmitters that directly influence your emotional state and mental well-being.
Stress Response
A balanced gut microbiome helps regulate your body's stress response and reduces anxiety through the gut-brain axis.
Mental Clarity
Optimal gut health supports cognitive function, focus, and mental clarity by reducing inflammation and supporting neurotransmitter production.
Supporting Your Gut Bacteria for Better Mental Health
Foods That Support Serotonin Production:
- •Fermented foods ( kefir, sauerkraut, kimchi)
- •Prebiotic fiber (bananas, onions, garlic, asparagus)
- •Omega-3 rich foods (fatty fish, walnuts, flaxseeds)
- •Tryptophan-rich foods (turkey, eggs, nuts, seeds)
Lifestyle Factors:
- •Reduce stress through meditation and mindfulness
- •Get adequate sleep (7-9 hours per night)
- •Exercise regularly to support gut motility
- •Avoid antibiotics unless absolutely necessary
Remember: When you take care of your gut health, you're not just improving digestion—you're directly supporting your mental health, mood, and overall quality of life. This is why alternative medicine emphasizes gut health as a foundation for total wellness.